Abstract
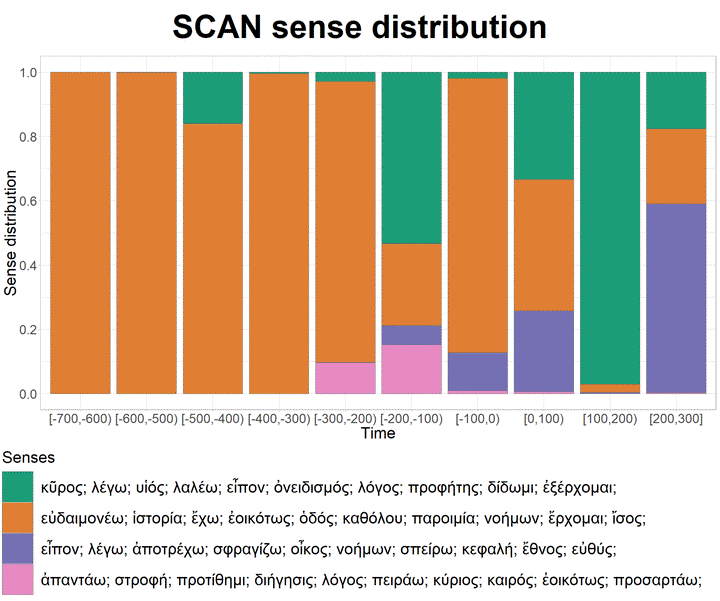
Language is a complex and dynamic system. If we consider word meaning, which is the scope of lexical semantics, we observe that some words have several meanings, thus displaying lexical polysemy. In this article, we present the first phase of a project that aims at computationally modelling Ancient Greek semantics over time. Our system is based on Bayesian learning and on the Diorisis Ancient Greek corpus, which we have built for this purpose. We illustrate preliminary results in light of expert annotation, and take this opportunity to discuss the role of computational systems and human analysis in a complex research area like historical semantics.
Type